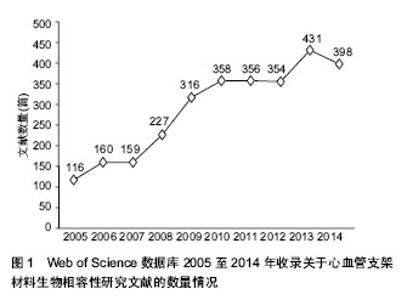
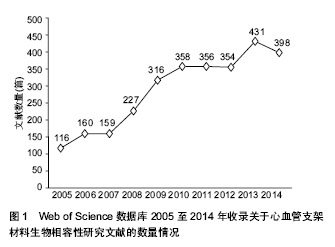
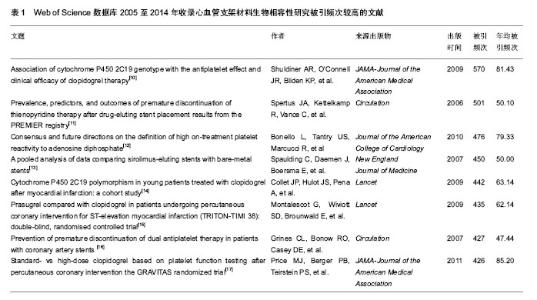
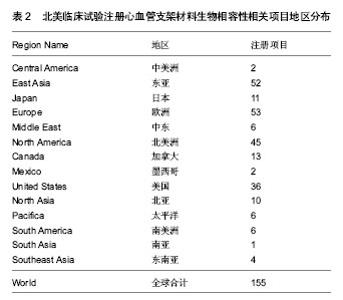
| [1] 袁晋青,高润霖,史瑞文,等.猪冠状动脉内金属支架蛋白涂层的生物相容性研究[J].中国循环杂志,1998,13(5):271-273.
[2] 朱建国,崔长综,兰燕平,等.犬冠状动脉内植入国产铂-铱合金(Pt-Ir)支架的实验研究[J].西安医科大学学报,2000,21(3):207-210.
[3] 聂晓敏,李庚山,江洪,等.犬冠状动脉内血浆包膜支架的生物相容性研究[J].心脏杂志,2002,14(3):184-186.
[4] 沈阳,王贵学,全学军,等.NiTi合金血管内支架表面改性及其生物相容性研究[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2006,30(1):3-7.
[5] Leng YX, Chen JY, Huang N, et al. The biocompatibility of the tantalum and tantalum oxide films synthesized by pulse metal vacuum arc source deposition. Nucl Instr and Meth in Phys Res. 2006;242:30.
[6] 庞景安.科学计量研究方法论[M].北京:科学技术文献出版社,1999.
[7] 周静怡,孙坦.基于Web of Science的数字图书馆研究论文定量分析[J].情报科学,2005,23(10):1521-1525.
[8] 岳洪江,刘思峰,梁立明.我国对技术创新的关注与研究—基于24年的文献计量分析[J].科研管理,2008,(5):43-52.
[9] Nason GJ, Tareen F, Mortell A. The top 100 cited articles in urology: An update. Can Urol Assoc J. 2013;7(1-2):E16-24.
[10] Shuldiner AR, O'Connell JR, Bliden KP, et al. Association of cytochrome P450 2C19 genotype with the antiplatelet effect and clinical efficacy of clopidogrel therapy. JAMA. 2009; 302(8): 849-857.
[11] Spertus JA, Kettelkamp R, Vance C, et al. Prevalence, predictors, and outcomes of premature discontinuation of thienopyridine therapy after drug-eluting stent placement: results from the PREMIER registry. Circulation. 2006;113(24): 2803-2809.
[12] Bonello L, Tantry US, Marcucci R, et al. Consensus and future directions on the definition of high on-treatment platelet reactivity to adenosine diphosphate. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 56(12):919-933.
[13] Spaulding C, Daemen J, Boersma E, et al. A pooled analysis of data comparing sirolimus-eluting stents with bare-metal stents. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(10):989-997.
[14] Collet JP, Hulot JS, Pena A, et al. Cytochrome P450 2C19 polymorphism in young patients treated with clopidogrel after myocardial infarction: a cohort study. Lancet. 2009;373(9660): 309-317.
[15] Montalescot G, Wiviott SD, Braunwald E, et al. Prasugrel compared with clopidogrel in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction(TRITON-TIMI 38): double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373(9665):723-731.
[16] Grines CL, Bonow RO, Casey DE Jr, et al.Prevention of premature discontinuation of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery stents: a science advisory from the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, American College of Surgeons, and American Dental Association, with representation from the American College of Physicians. J Am Dent Assoc. 2007;138(5): 652-655.
[17] Price MJ, Berger PB, Teirstein PS, et al. Standard- vs high-dose clopidogrel based on platelet function testing after percutaneous coronary intervention: the GRAVITAS randomized trial. JAMA. 2011;305(11):1097-1105. |